Proper GC maintenance is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable results. Gas chromatography is a widely used analytical technique for separating and quantifying volatile compounds in various samples. From environmental monitoring to pharmaceutical analysis, gas chromatography plays a pivotal role across various disciplines.
This article presents an overview of gas chromatograph maintenance, encompassing essential tips and strategies to enhance instrument performance, extend its lifespan, and minimize downtime. By implementing maintenance best-practices, researchers and analysts can achieve consistent and high-quality results in their analytical work.
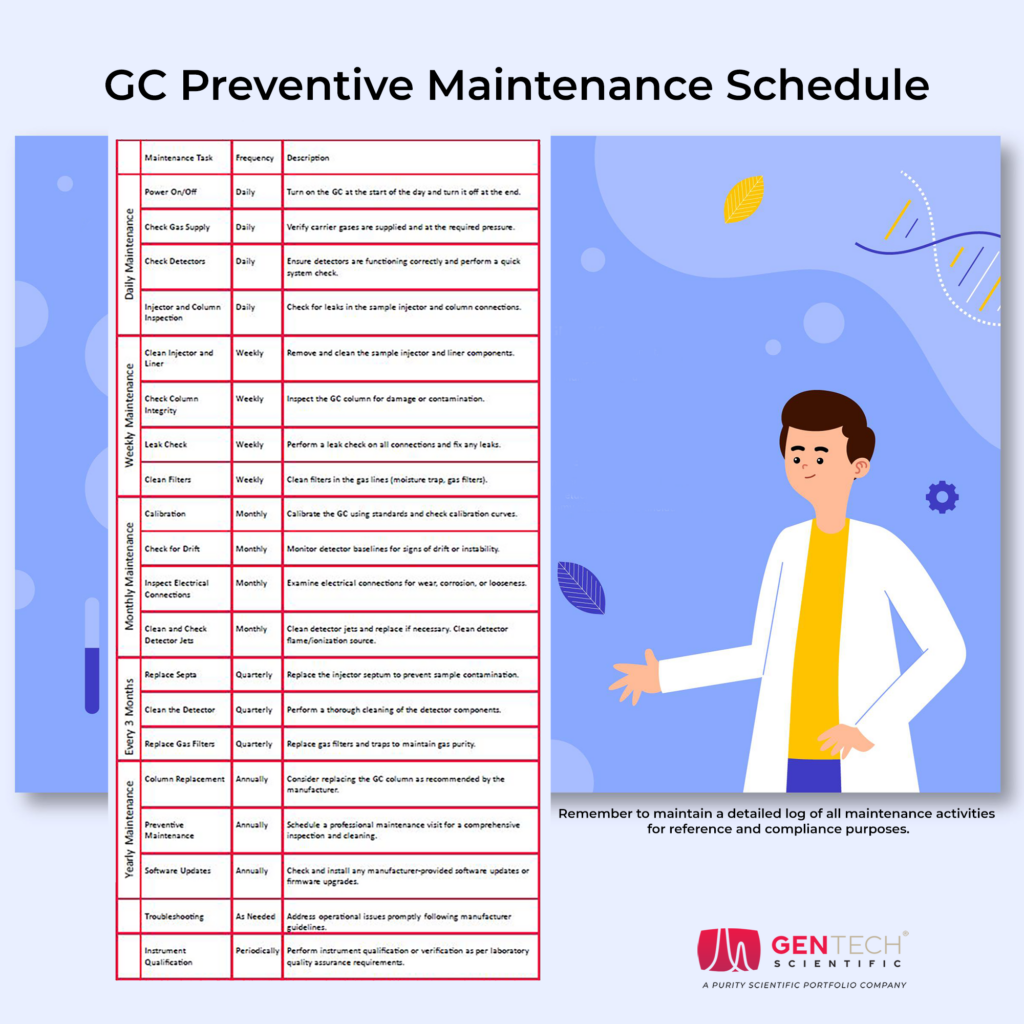
Routine Maintenance
- Visual Inspection: Regular visual inspections should be conducted to identify any visible signs of wear, corrosion, or contamination. This includes examining the injector, column, and detector for any anomalies that might affect instrument performance.
- Cleaning: Routine cleaning of critical components, such as the injector and detector, is vital to prevent cross-contamination and residue buildup. Using appropriate solvents and cleaning techniques can help maintain the chromatograph’s sensitivity and accuracy.
- Gas Supply Cleanliness & Leak Checks: Monitoring and maintaining a stable gas supply is crucial for consistent performance. Regularly check gas pressure and quality to ensure optimal chromatographic separations. Regularly inspect and replace gas traps to prevent impurities from reaching the GC system. Ensure that gas cylinders are properly stored, secured, and maintained. If your GC uses gas generators, follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance and filter replacement to ensure a clean and consistent gas supply. Regular leak checks should be performed on gas lines, fittings, and connections to prevent leaks that could affect the integrity of the analysis and compromise safety.
Preventive Maintenance
- Column Use & Care: The chromatographic column is a critical component that requires special attention. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for column installation, conditioning, and storage to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Properly install GC columns according to manufacturer guidelines. Use the recommended torque when connecting the column to the inlet and detector. Avoid exposing columns to excessive temperatures, pressure, or contamination. Regularly clean the inlet and detector interfaces to prevent buildup. If applicable, use guard columns to protect the analytical column from sample matrix and other contaminants. Replace guard columns as needed.
- Autosampler Maintenance:
- Inspect and clean or replace autosampler needles periodically to prevent carryover and ensure accurate injections.
- Establish and execute proper wash routines for the autosampler to minimize cross-contamination between samples.
- Inlet Maintenance:
- Replace the inlet liner regularly to prevent sample decomposition, reduce contamination, and ensure consistent peak shapes.
- Inspect and replace septa as needed to prevent leaks and contamination.
- Detector Maintenance: Detectors need periodic maintenance. This includes cleaning the detector’s components, checking for leaks, and calibrating the detector for accurate signal responses.
- Flame Ionization Detector (FID): Regularly clean the FID jet and collector to maintain sensitivity and minimize baseline noise.
- Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD): Check the reference and sample cells for cleanliness and proper functioning. Adjust bridge balance as necessary.
- Electron Capture Detector (ECD): Replace the ECD filament periodically and ensure proper gas flows for sensitivity and stability.
- Calibration and Performance Verification: Regularly calibrate the gas chromatograph using certified reference standards to ensure accurate quantification. Additionally, verify the system’s performance through routine tests, such as analyzing known samples or using system suitability standards.
Advanced Maintenance
- Column Backflushing: Implement column backflushing to remove non-volatile residues that accumulate at the column inlet. This technique helps prolong the column’s lifespan and maintain consistent performance.
- Purge and Trap: For trace-level analysis, consider using a purge and trap system to concentrate volatile compounds before injection. Regular maintenance of this system is essential for optimal sensitivity and reproducibility.
Software Updates & Data Management
- Regularly update the chromatography software to access the latest features and bug fixes. Implement robust data management practices, including regular backups, to safeguard valuable analytical data.
In Conclusion…
Effective maintenance of gas chromatographs is paramount for achieving reliable and accurate analytical results. By following routine maintenance practices, conducting preventive procedures, and addressing more advanced maintenance needs, researchers and analysts can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of their gas chromatograph systems. Adhering to these practices will enhance data quality, minimize downtime, and contribute to the overall success of analytical endeavors.
Are GC problems getting you down? Troubleshooting efforts not working? Contact GenTech Scientific‘s team of experts for help and get your instrument up and running!
Check out our extensive inventory of high quality, expertly refurbished gas chromatography instruments, and upgrade your lab at a fraction of the cost of new!