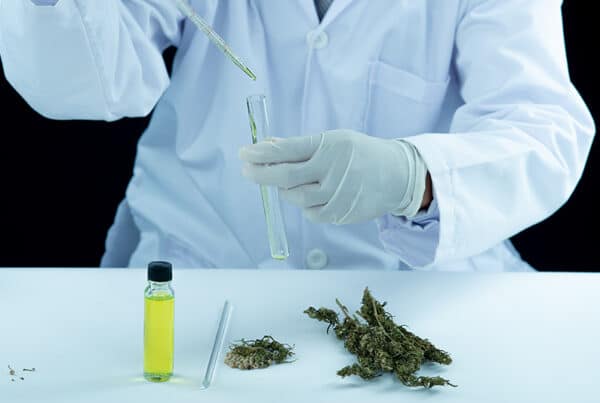
Cannabis use is more widespread than ever, which means that cannabis testing is more important than ever. Our explainer will go through a brief history of cannabis analytical testing and some common forms of cannabis analysis.
Origins of Cannabis Analytical Testing
The origins of cannabis analytical testing are strongly linked to the application of medical marijuana. Historians have found evidence of cannabis being used by early civilizations as early as 5,000 years ago, and as a medicinal product as far back as 400 AD.
However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that scientists began to study the flower and its possible medicinal qualities. Although it was federally restricted in 1937, analytical cannabis testing provided evidence that doctors could use cannabis to treat certain illnesses and relieve pain in patients.
Some common illnesses that doctors utilize cannabis for include:
- HIV/AIDS
- Cancer
- Parkinson’s
- Alzheimer’s
- Glaucoma
Cannabis Legalization and Testing Advancements
In 1996, California became the first US state to legalize the use of cannabis in a medical capacity under a physician’s supervision. The legalization breakthrough opened the door for further cannabis testing. It forced government agencies to regulate and test the product to ensure its safety and learn more about the flower.
As of this writing, 39 US states allow cannabis for medical purposes, and 18 have legalized it for recreational use. The growth of cannabis use means advancements in testing technology and techniques as more states invest resources into the industry.
Types of Cannabis Analytic Testing
Numerous types of cannabis analytical testing exist, each requiring specific cannabis lab equipment that has developed as the flower’s popularity has grown. Three significant areas of analysis are cannabinoid analysis, terpene analysis, and strain analysis.
Cannabinoid Analysis
Cannabinoid analysis entails identifying and labeling the compounds of the cannabis flower, like THC, CBD, and CBN. THC is the compound that gives cannabis its psychoactive effect, while CBD is different and does not affect users as dramatically.
CBN (cannabinol) is somewhere in between THC and CBD. It doesn’t have the same potency as THC, but if consumed in larger doses, it can cause psychoactive effects. Cannabinoid analysis can be done via gas or liquid chromatography.
Terpene Analysis
Terpenes are compounds found in flowers and plants that give them a unique fragrance. Different terpenes cause some cannabis flowers to smell or taste different than others.
They’re also the compound that gives the cannabis flower some of its medicinal properties. Scientists can analyze the terpenes of cannabis with gas or liquid chromatography techniques.
Strain Analysis
Strain analysis is when chemists identify the strain of a cannabis flower, essentially whether it’s a pure variety of the plant or a mixed hybrid. The most common technique for this kind of analysis is a polymerase chain reaction because identifying strains is similar to copying and generating DNA sequences.
That was just a brief history of cannabis analytical testing, but there’s much to the science. If you have questions about cannabis lab equipment, consult with the experts at GenTech Scientific.