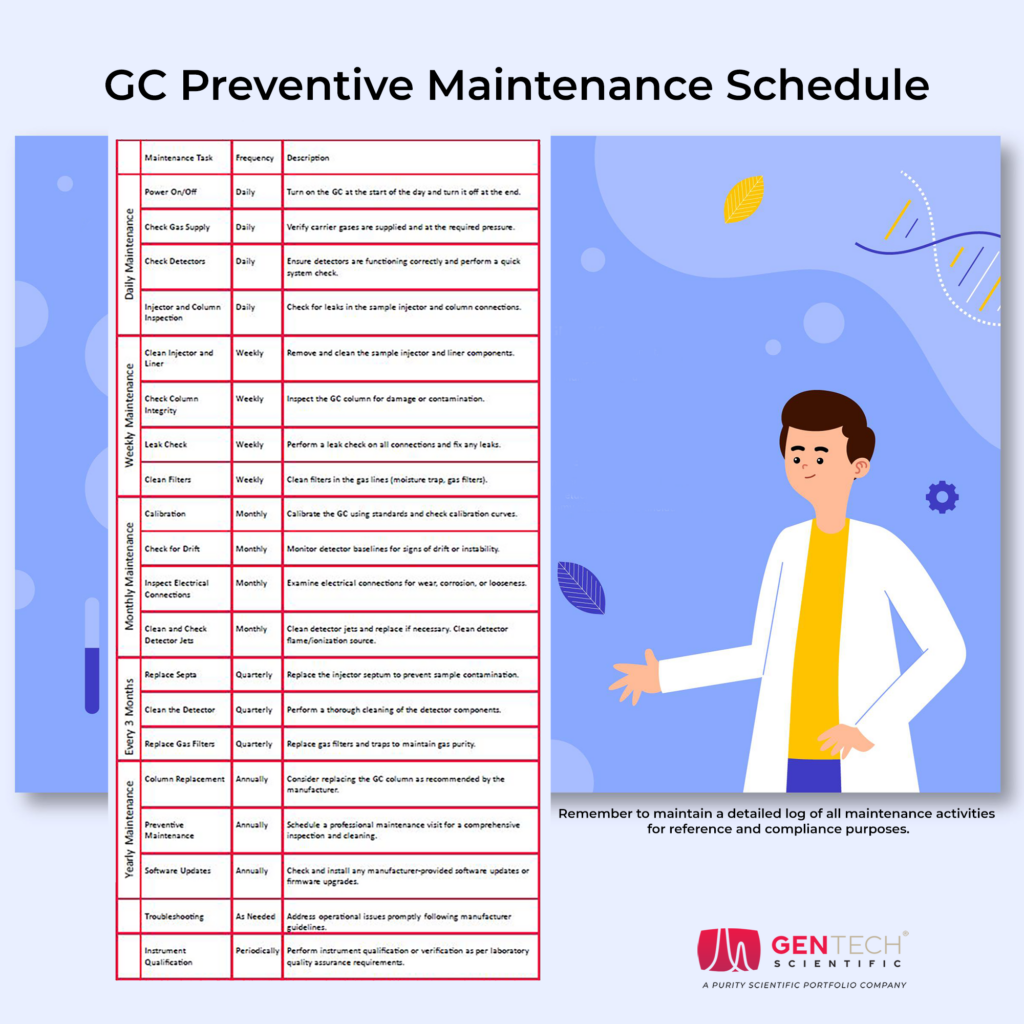
As scientists and lab managers well know, gas chromatography (GC) is a fundamental analytical technique widely used for separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in a sample. To ensure the accuracy and reliability of your GC results, it’s crucial to establish a robust preventive maintenance routine. Here is an overview of the essential considerations for maintaining your GC instrument in optimal working condition.
Why Preventive Maintenance Matters
Preventive maintenance is the key to extending the lifespan of your GC instrument and maintaining data accuracy. Here are some compelling reasons why preventive maintenance is essential:
- Consistency in Results. Regular maintenance helps minimize variations in your analyses. Proper maintenance ensures your GC system performs consistently over time, and delivers precise and reliable results.
- Longer Instrument Lifespan. Proper care can significantly extend the lifespan of your GC instrument, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Cost Savings. Preventive maintenance is more cost-effective than reactive repairs, as it helps identify and address issues before they become major problems.
- Safety. Ensuring the integrity of your GC system minimizes the risk of accidents or instrument malfunctions that can compromise safety in the laboratory.
Best Practices
Establish a Maintenance Schedule
- Routine Checkups. Create a maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations. Typically, GC systems require routine checkups every three to six months, but your specific instrument and usage may warrant more frequent maintenance.
- Keep Records. Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, including dates, tasks performed, and any issues identified. This documentation helps track the instrument’s history and aids in troubleshooting.
External Maintenance
- Cleanliness. Keep the exterior of your GC instrument clean and free from dust, spills, or chemical residues. Use mild solvents or specialized cleaning solutions recommended by the manufacturer.
- Ventilation. Ensure proper ventilation and a dust-free environment for your GC system. Adequate airflow prevents overheating and reduces the risk of contamination.
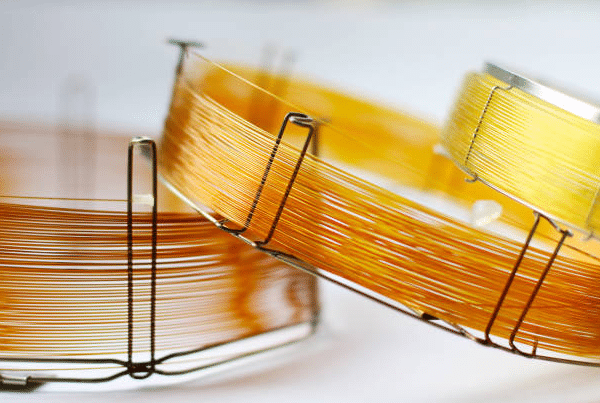
Column Care
- Column Inspection. Regularly inspect the GC column for signs of wear or damage. Replace the column when necessary to maintain accurate separations.
- Column Installation. Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper column installation. Pay close attention to column connections, ferrules, and septa to prevent leaks.
Detector Maintenance
- FID and TCD. For Flame Ionization Detectors (FID) and Thermal Conductivity Detectors (TCD), clean and maintain the detector components as recommended. Check for leaks and replace worn or damaged parts promptly.
- MS Detectors. If your GC system includes Mass Spectrometry (MS) detectors, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance, including vacuum system checks and ion source cleaning.
Injection System
- Sample Syringe. Regularly inspect and clean the sample syringe or injection port. Replace septa as needed to prevent contamination and sample carryover.
- Inlet Maintenance. Clean and maintain the inlet system, including liners and seals, to ensure precise sample introduction and minimize system downtime.
Gas Supply
- Gas Sources. Monitor gas sources and pressures regularly. Replace gas cylinders or refill gas supplies as required to maintain stable carrier gas flows.
- Gas Lines. Inspect and clean gas lines and regulators to prevent blockages or leaks that could disrupt analyses.
Software and Calibration
- Software Updates. Keep GC control software up to date with the latest patches and updates from the manufacturer.
- Calibration Checks. Regularly calibrate your GC system using standard calibration mixtures to ensure accurate quantification.
Safety Considerations
- Safety Checks. Prioritize safety by inspecting safety features like gas leak detectors, flame sensors, and emergency shut-off mechanisms.
- Training. Ensure that laboratory personnel are well-trained in handling GC equipment safely and are familiar with emergency protocols.
Regular System Checks
- System Diagnostics. Use built-in diagnostic tools provided by the manufacturer to identify potential issues before they affect your analyses.
- Performance Verification. Periodically run performance verification tests to confirm the accuracy and precision of your GC system.
Collaborate with Experts
- Manufacturer Support. Establish a relationship with the instrument manufacturer or a certified service provider. Seek their guidance for complex maintenance tasks or repairs.
- Training. Invest in training programs for your lab technicians to enhance their knowledge and skills in GC maintenance and troubleshooting.
Protect Your Investment
By following these best practices for GC preventive maintenance, you can ensure the longevity, reliability, and accuracy of your gas chromatography system. Incorporate these guidelines into your laboratory’s standard operating procedures to minimize downtime, reduce costs, and produce high-quality analytical results consistently. Remember that a well-maintained GC instrument is the foundation of successful scientific research and analysis in your laboratory.